User Guide
Welcome to the User Guide of Teaching Assistant!
Are you a JC/Secondary school teacher, having troubles keeping track of all your consultations, meetings and your students’ contacts? No worries! Our application, Teaching Assistant will provide an all-in-one platform for you to organise your entries (schedules) and contacts!
We target JC/Secondary school teachers as they are the teachers who have a greater need to contact their students compared to primary school schools, yet do not have a standardised platform for communication unlike teachers in tertiary schools.
Teaching Assistant mainly uses a Command Line Interface (CLI). For users who type fast, they can use this application more efficiently than other applications that heavily use Graphical User Interface (GUI).
If you are interested, jump to Quick Start to learn how to learn how to start using Teaching Assistant.
An image of our UI is shown below!
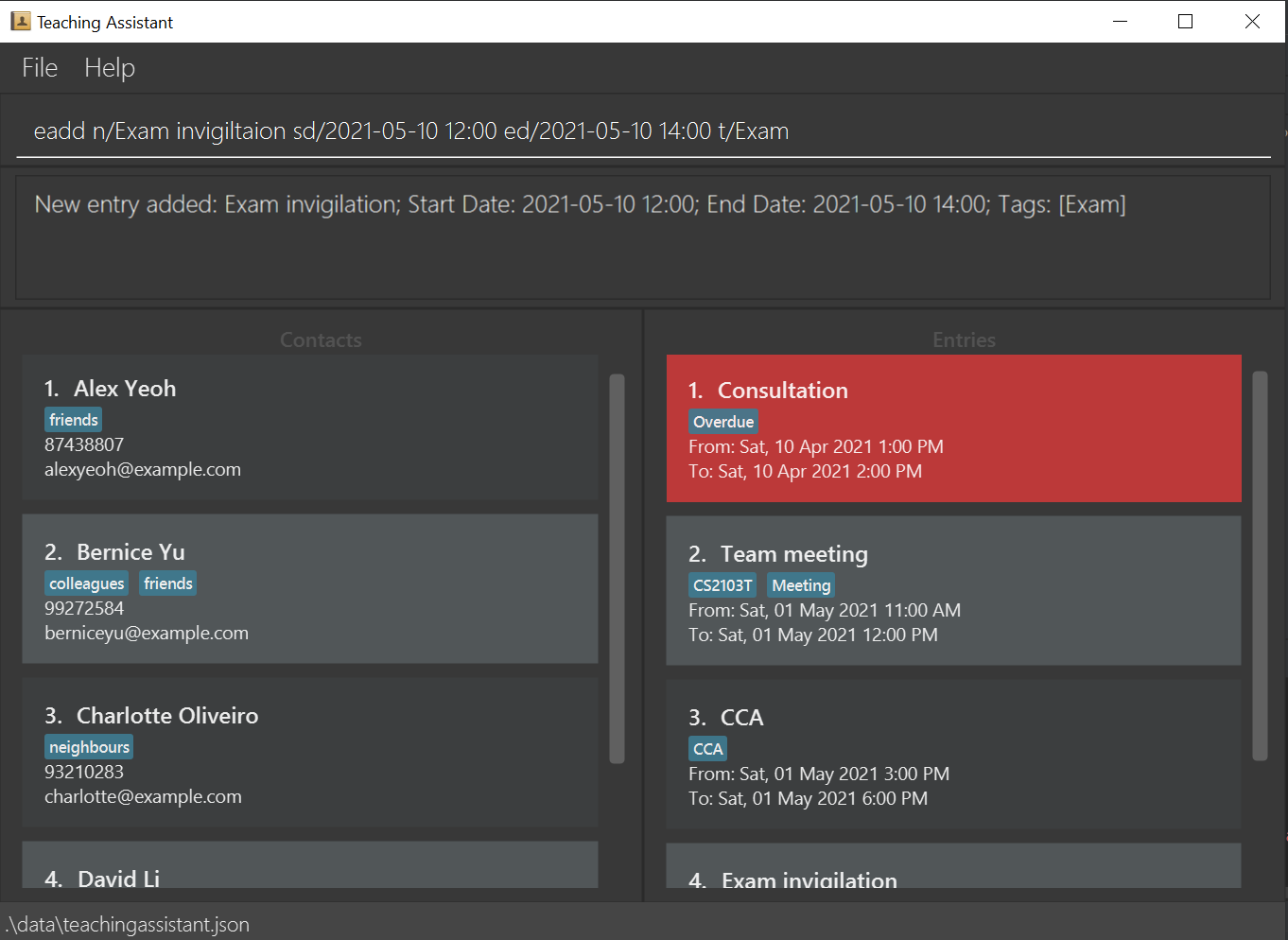
Quick Start
- Ensure you have Java 11 installed in your computer. You may install it here.
- Download the latest
teachingAssistant.jarhere. - Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your Teaching Assistant.
- Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI similar to the image above should appear.
- Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
Some example commands you can try:
-
clist: Lists all contacts in Teaching Assistant. -
cadd n/Danny Tan p/98765432 e/danny@email.com: Adds a contact namedDanny Tanto Teaching Assistant. -
efind consultation: Finds an entry namedconsultationor entries that haveconsultationin their names in Teaching Assistant. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
- Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Structure of the User Guide
Worried about how tedious it will be to read this document? Not to worry! We have structured this User Guide in a way that makes it easy and quick for you to find what you need. In this next subsection, Reading this User Guide, you can find some tips we have on how to read this guide. The next section, Features, documents the main functionalities of Teaching Assistant and how to use them.
The main functions of Teaching Assistant can be summmarised as the following:
- Contact management
- Entry (schedules) management
If you prefer a brief overview of all the commands, head over to command summary which provides you with a table of all available commands.
Reading this User Guide
This section introduces you to some technical terms and syntax that will be used throughout the User Guide. You may want to read through this section thoroughly first before moving on to the next sections.
Terminology
The image of our GUI is shown below, annotated with descriptions of each GUI component we refer to in this User Guide.
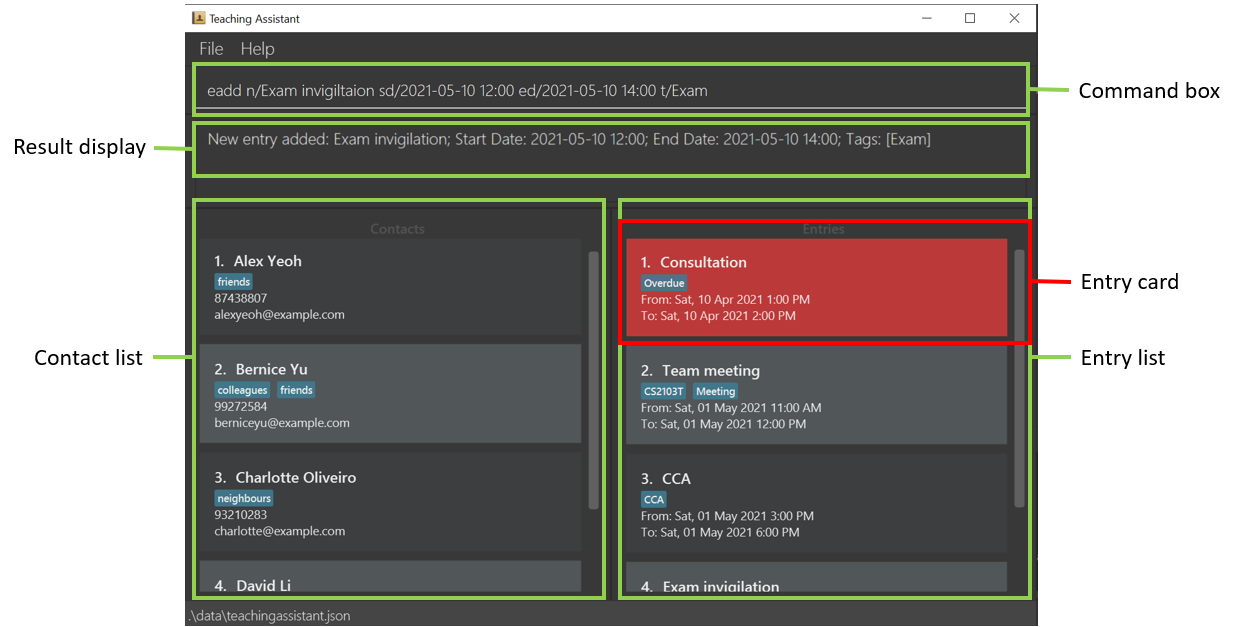
The table below defines some technical terminology used throughout the User Guide.
| Terms | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CLI | Command Line Interface. In the context of Teaching Assistant, this refers to the command box where you can type your commands. |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface. It refers to the part of the application you interact with through graphical features such as buttons. |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation. Your Teaching Assistant data is stored as a JSON file format. You can find out more on their official website here! |
General Syntax
The table below explains the general syntax used throughout the User Guide.
| Syntax | Meaning |
|---|---|
command |
This markup is used to specify text that can be entered into the command box. |
| This icon indicates that the following text is a tip. | |
| This icon indicates that the following text is a warning. | |
| This icon indicates that the following text is a note. |
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
- Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user. e.g. incadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used ascadd n/Danny Tan. - Items in the square brackets are optional. Users can choose to leave the field empty.
- Items with
...after them can be used multiple times including zero times. e.g.[t/TAG]...can be used as ` ` (i.e. 0 times), t/friend, t/friend t/family etc. - Parameters can be in any order. e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME p/NUMBER,p/NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. - If a parameter is expected only once in the command but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of
the parameter will be taken. e.g. if you specify
p/12341234 p/56785678, onlyp/56785678will be taken. - Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored. e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
Viewing help: help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
Format: help
Breakdown:
- Command word -
help
Scenario: You are using Teaching Assistant but forget the formats of the commands you want to execute. This command is the only one you need to remember! It will bring you to this document.
Adding a contact: cadd
Adds a contact into Teaching Assistant.
Format: cadd n/NAME p/NUMBER e/EMAIL [t/TAG]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
cadd - Prefixes -
n/,p/,e/,t/ - Parameters -
NAME,NUMBER,EMAIL,TAG
Example(s):
cadd n/Danny Tan p/98765432 e/danny@email.com t/student t/english t/consultation1cadd n/Amy Yeoh p/12345678 e/amy@email.com t/Colleague t/OwesMoney t/meeting1
Scenario: You want to save the contact details of your students so that you can easily obtain their details when you want to reach out to them.
Finding a contact: cfind
Finds all contacts whose name contain all of the specified keywords and displays them as a list.
Format: cfind KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
cfind -
Parameters -
KEYWORD,MORE_KEYWORDS - Only names are searched.
- The search is case-insensitive e.g.
amywill matchAmy. - Only full words will be matched e.g.
Danwill not matchDanny. - Only contacts matching all keywords will be returned (i.e. AND search). E.g.
Danny Tanwill only returnDanny Tan. - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Danny Tanwill matchTan Danny.
Example(s):
-
cfind DannyreturnsdannyandDanny Tan -
cfind amy yeohreturns onlyAmy Yeoh
Below is an illustration of entering cfind yeoh on a sample Teaching Assistant:
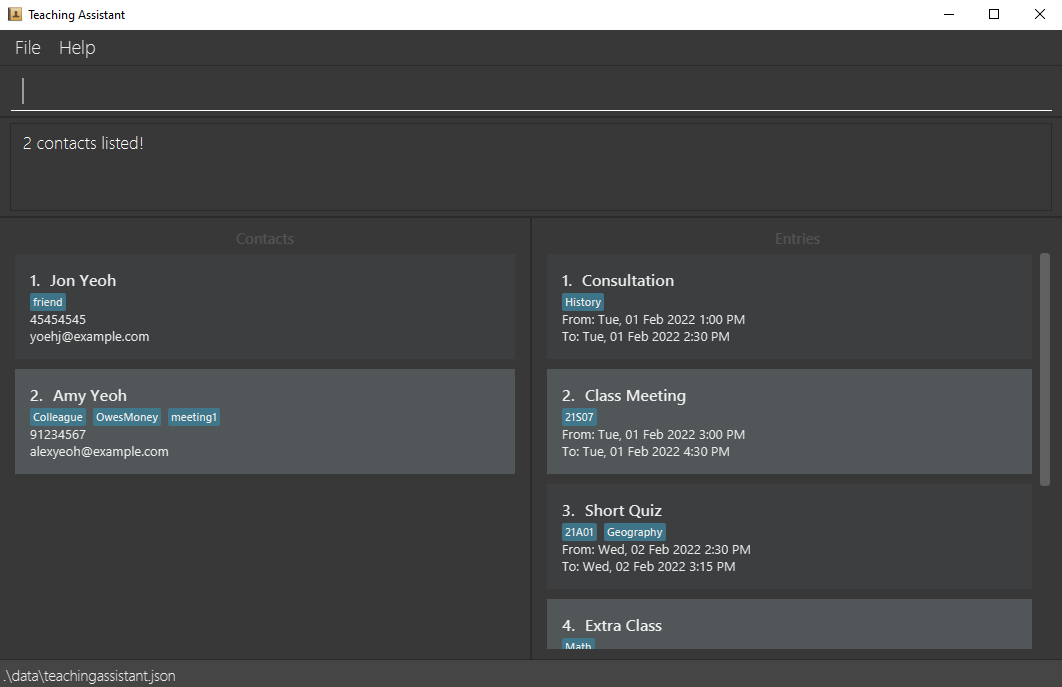
Scenario: Your student had booked a consultation with you and you want to find his/her contact details by name without scrolling through the entire contact list so that you can remind him/her of the arrangement as the date of the consultation draws nearer.
Filter contact tags: cfilter
Filters all contacts that have the tags of the specified keywords and displays them as a list with index numbers.
Format: cfilter KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
cfilter -
Parameters -
KEYWORD,MORE_KEYWORDS - Only tags are searched.
- The filtering is case-insensitive e.g.
Studentwill matchstudent. - Only full words will be matched e.g.
Friendwill not matchFriends. - If more than one keyword is provided, only contacts with all the keywords provided will be displayed.
E.g.
filter colleagues friendswill only return a contact with both tagscolleaguesandfriends. Contacts with only one of the 2 keywords will not be displayed. - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
colleagues friendswill matchfriends colleagues.
Example(s):
cfilter student englishcfilter colleague
Scenario: Your students have decided on the roles and responsibilities they will be taking up in your class (e.g. chairperson, english representative). You can add a tag to their contact to identify their roles. Then, you can find their contact details easily by filtering contacts via tags.
Editing a contact: cedit
Edits an existing contact with the specified index in Teaching Assistant.
Format: cedit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [t/TAG]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
cedit - Prefixes -
n/,p/,e/,t/ -
Parameters -
INDEX,NAME,NUMBER,EMAIL,TAG -
INDEXrefers to the index numer shown in the displayed entry list. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer 1,2,3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the contact will be removed i.e. adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the contact’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it.
Example(s):
-
cedit 1 p/91234567 e/alexyeoh@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the contact corresponding to index 1 and top/91234567andalexyeoh@example.comrespectively. -
cedit 1 n/Bernice Yu Xiao Ling t/Edits the name of the contact corresponding to index 1 to beBernice Yu Xiao Lingand clears all existing tags.
Below is an illustration of entering cedit 1 n/Bernice Yu Xiao Ling t/ into a sample Teaching Assistant:
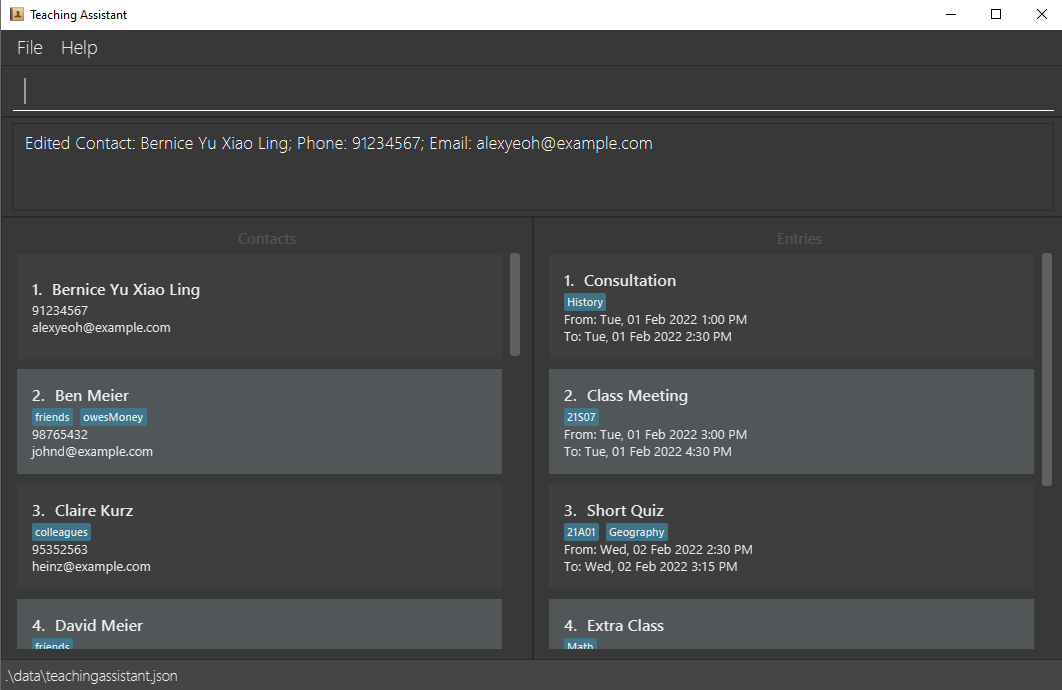
Scenario:
Your student had recently changed his/her phone number and you want to update his/her contact details without the
hassle of deleting his/her old contact and then subsequently adding a new updated contact.
Listing contacts: clist
Lists all the contacts in Teaching Assistant.
Format: clist
Breakdown:
- Command word -
clist
Scenario: You want to look at all the contacts you have saved.
Deleting a contact: cdelete
Deletes an existing contact with the specified index in Teaching Assistant.
Format: cdelete INDEX
Breakdown:
- Command word -
cdelete -
Parameters -
INDEX -
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed contact list. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Example(s):
cdelete 1
Scenario: Your students have long graduated and you will not be contacting them anymore. You want to remove their contacts to make space for the contacts of your new students.
Adding an entry: eadd
Adds a new entry into Teaching Assistant.
Format: eadd n/NAME sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE [t/TAG]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
eadd - Prefixes -
n/,sd/,ed/,t/ -
Parameters -
NAME,START_DATE,END_DATE,TAG -
START DATEandEND DATEare in the formatyyyy-mm-dd HH:MM. -
START DATEshould be beforeEND DATE. - Entries cannot overlap. i.e. Entries with overlapping timings will not be added.
- Addition of entries which start and end in the past are allowed but the GUI will show a red entry card.
Example(s):
eadd n/meeting sd/2021-06-06 21:00 ed/2021-06-06 23:00 t/meeting t/needprepeadd n/consultation 1 sd/2021-06-07 22:00 ed/2021-06-07 23:00 t/consultation
Below is an illustration of entering eadd n/consultation 1 sd/2021-06-07 22:00 ed/2021-06-07 23:00 t/consultation
into a sample Teaching Assistant:
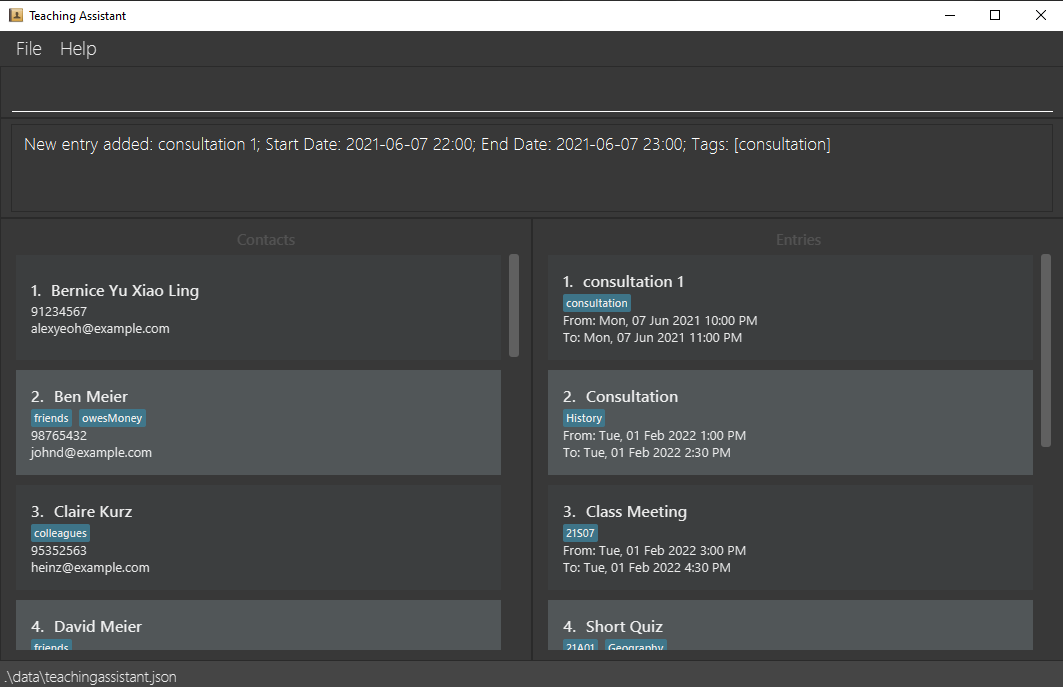
Scenario: You want to add entries into Teaching Assistant to keep track of your schedule.
Finding an entry: efind
Finds all entries whose name contain all of the specified keywords and displays them as a list.
Format: efind KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
efind -
Parameters -
KEYWORD,MORE_KEYWORDS - Only names are searched.
- The search is case-insensitive e.g.
meetingwill matchMeeting. - Only full words will be matched e.g.
meetingwill not matchmeetings. - Only entries matching all keywords will be returned (i.e. AND search). E.g.
meeting 1will only returnmeeting 1. - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
teaching assistantwill matchassistant teaching.
Example(s):
-
efind consultationreturnsconsultation 1andconsultation 2 -
efind consultation 2returns onlyconsultation 2
Scenario: You remember you added a school event entry into Teaching Assistant in the past but forgot its date. You can find an entry’s details by its name without scrolling through the entire entry list.
Filter entry tags: efilter
Filters all entries that have the tags of the specified keywords and displays them as a list.
Format: efilter KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
efilter -
Parameters -
KEYWORD,MORE_KEYWORDS - Only tags are searched.
- The filtering is case-insensitive e.g.
meetingwill matchMeeting. - Only full words will be matched e.g.
meetingwill not matchmeetings. - If more than one keyword is provided, only entries with all the keywords provided will be displayed.
E.g.
filter meeting needprepwill only return an entry with both tagsmeetingandneedprep. Entries with only one of the 2 keywords will not be displayed. - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
meeting needprepwill matchneedprep meeting.
Example(s):
efilter meetingefilter meeting needprep
Below is an example of entering efliter history into a sample Teaching Assistant:
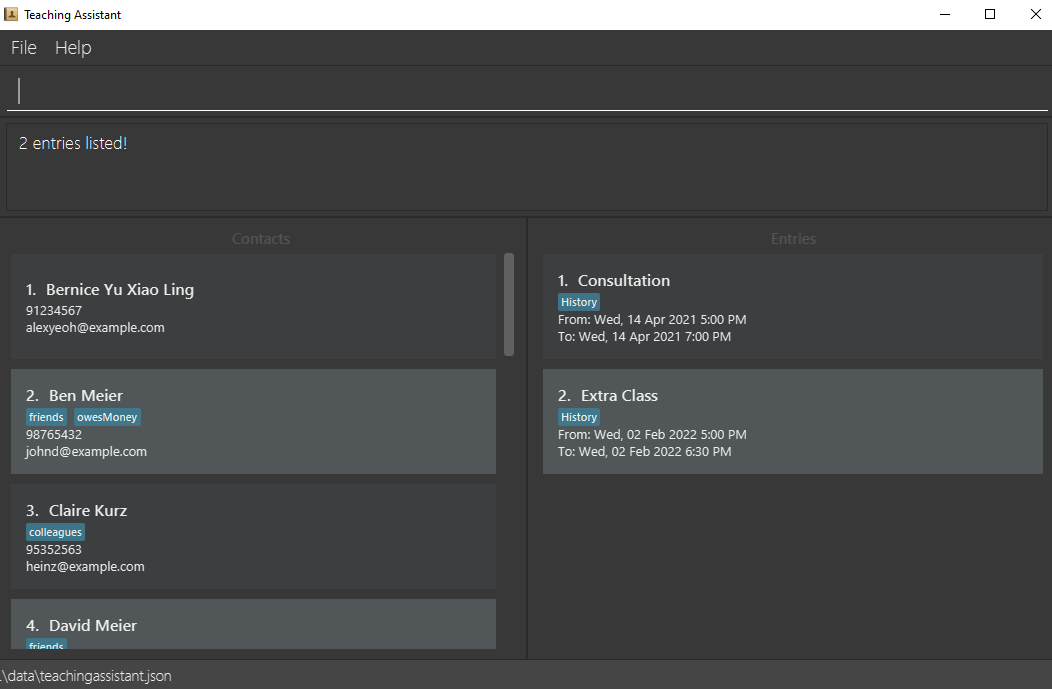
Scenario: You want to filter your entries via the consultation tag you have added to your entries in the past, so that you can plan ahead and prepare for your upcoming consultations.
Editing an entry: eedit
Edits an existing entry with the specified index in Teaching Assistant.
Format: eedit INDEX [n/NAME] [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE] [t/TAG]...
Breakdown:
- Command word -
eedit - Prefixes -
n/,sd/,ed/,t/ -
Parameters -
INDEX,NAME,START_DATE,END_DATE,TAG -
INDEXrefers to the index numer shown in the displayed entry list. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer 1,2,3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the entry will be removed i.e. adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the entry’s tags by typing t/ without specifying any tags after it.
Example(s):
-
eedit 1 sd/2021-06-07 13:00 ed/2021-06-07 14:00Edits the start and end dates of the entry corresponding to index 1 to be2021-06-07 13:00and2021-06-07 14:00respectively. -
eedit 1 t/Edits the entry corresponding to index 1 by clearing all existing tags.
Scenario: The Head of Department (HOD) just rescheduled a department meeting. You want to edit an entry’s start and end dates without first deleting it and then subsequently adding a new entry with the updated dates.
Listing entries: elist
Lists all entries in Teaching Assistant by displaying them as a list sorted by date. Entries can also be listed by day/week.
Format: elist [FORMAT]
Breakdown:
- Command word -
elist -
Parameters -
FORMAT - No argument: listing all entries
-
FORMATis only restricted to the following cases-
day: listing entries for today -
week: listing entries for today as well as the next 6 days
-
Example(s):
elistelist dayelist week
Below is an illustration of entering elist week into a sample Teaching Assistant (The current date is 2021-04-12):
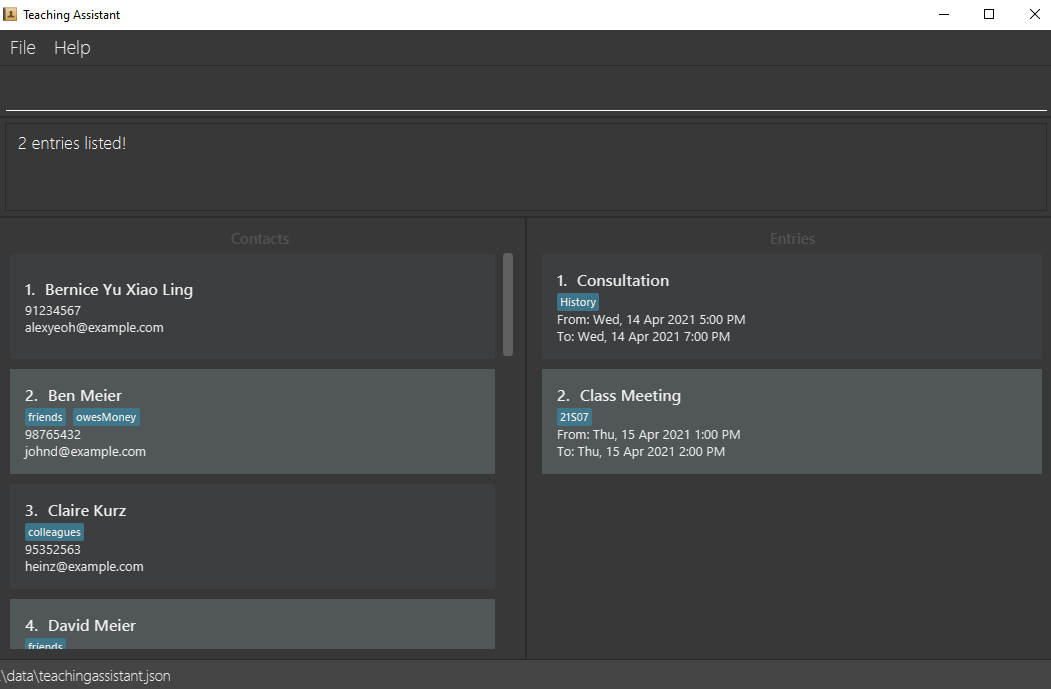
Scenario: You want to see what is in store for you today so that you can mentally prepare yourself for the busy day ahead.
Checking if time interval is free: free
Indicates if an interval is free. If free, a message indicating that will be shown. If not, entries occupying that interval will be shown in the entry list.
Format: free sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE
Breakdown:
- Command word -
free - Prefixes -
sd/,ed/ -
Parameters -
START_DATE,END_DATE -
START DATEandEND DATEare in the formatyyyy-mm-dd HH:MM. -
START DATEshould be beforeEND DATE.
Example(s):
-
free sd/2021-06-06 21:30 ed/2021-06-06 22:30if the time interval is free, entry list will be empty and “You’re free!” message is shown. If not, a message “Sorry, you’re not free. Entries occupying that time interval listed below!” will be shown, accompanied by occupying entries in the entry list.
Below is an illustration of entering free sd/2021-06-06 21:30 ed/2021-06-06 22:30 into a sample Teaching Assistant
where there are no entries between the given timeslot:
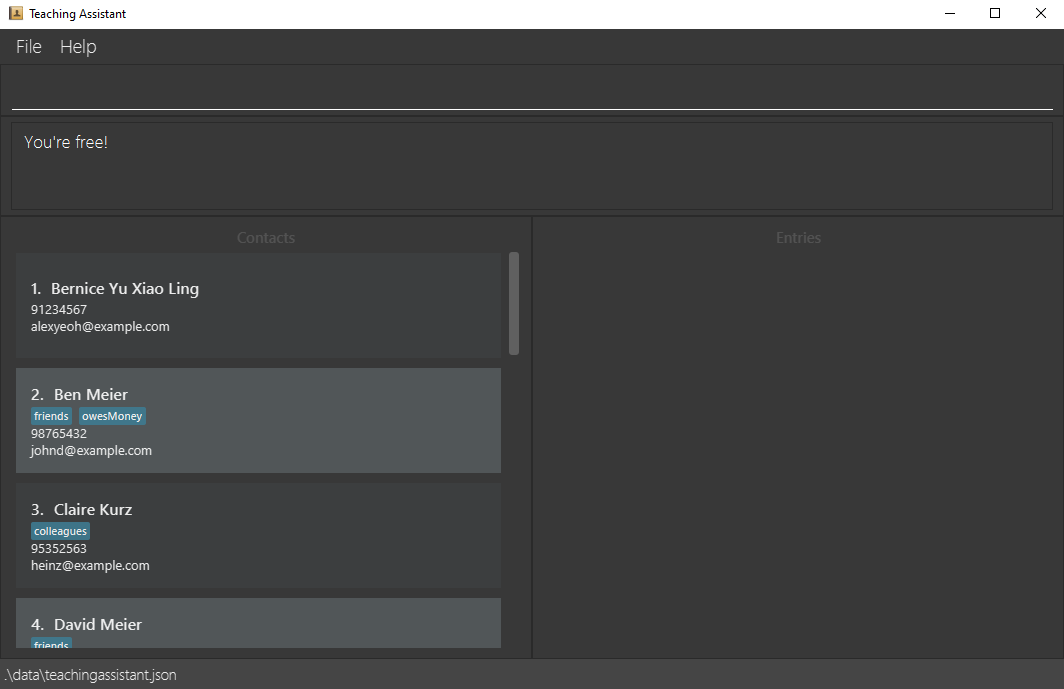
Scenario: Your student just approached you to book a consultation and asks if you are available at a specific timing.
Deleting an entry: edelete
Deletes an existing entry with the specified index in Teaching Assistant.
Format: edelete INDEX
Breakdown:
- Command word -
edelete -
Parameters -
INDEX -
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed contact list. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Example(s):
edelete 1
Scenario: A school event you are involved in has been cancelled because of Covid-19 restrictions. You want to delete this entry from your schedule.
Clearing overdue entries: eclear
Clears all entries that are overdue.
Format: eclear
Breakdown:
- Command word -
eclear - An Entry is considered overdue if it has an end date and time that is before current date and time.
Scenario: You still have a lot of entries from the past that you no longer need, and want to quickly remove those outdated entries to not clutter the entry list.
Clearing all data: clear
Clears all contacts and entries from Teaching Assistant.
Format: clear
Breakdown:
- Command word -
clear
Scenario: You opened Teaching Assistant for the first time and want to start using it. You want to clear the sample data given before you proceed.
Exiting the program: exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Breakdown:
- Command word -
exit
Scenario: You survived yet another hectic day! Use this command to exit the app.
Saving the data
Teaching Assistant data is saved in the hard disc automatically after any command that changes the data is executed. There is no need to save data manually.
Editing the data file
Teaching Assistant data is saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/teachingassistant.json. Advanced users are
welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer? A: Install Teaching Assistant in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous Teaching Assistant home folder.
Command summary
Others
| Action | Format |
|---|---|
| View all commands | help |
| Clear | clear |
| Exit | exit |
Contacts
| Action | Format |
|---|---|
| Add | cadd n/NAME p/NUMBER e/EMAIL [t/TAG]... |
| Find | cfind KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]... |
| Filter tags | cfilter KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]... |
| Edit | cedit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [t/TAG]... |
| List | clist |
| Delete | cdelete INDEX |
Entries
| Action | Format |
|---|---|
| Add | eadd n/NAME sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE [t/TAG]... |
| Find | efind KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]... |
| Filter tags | efilter KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]... |
| Edit | eedit INDEX [n/NAME] [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE] [t/TAG]... |
| List | elist [FORMAT] |
| Check if free | free sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE |
| Delete | edelete INDEX |
| Clear overdue entries | eclear |